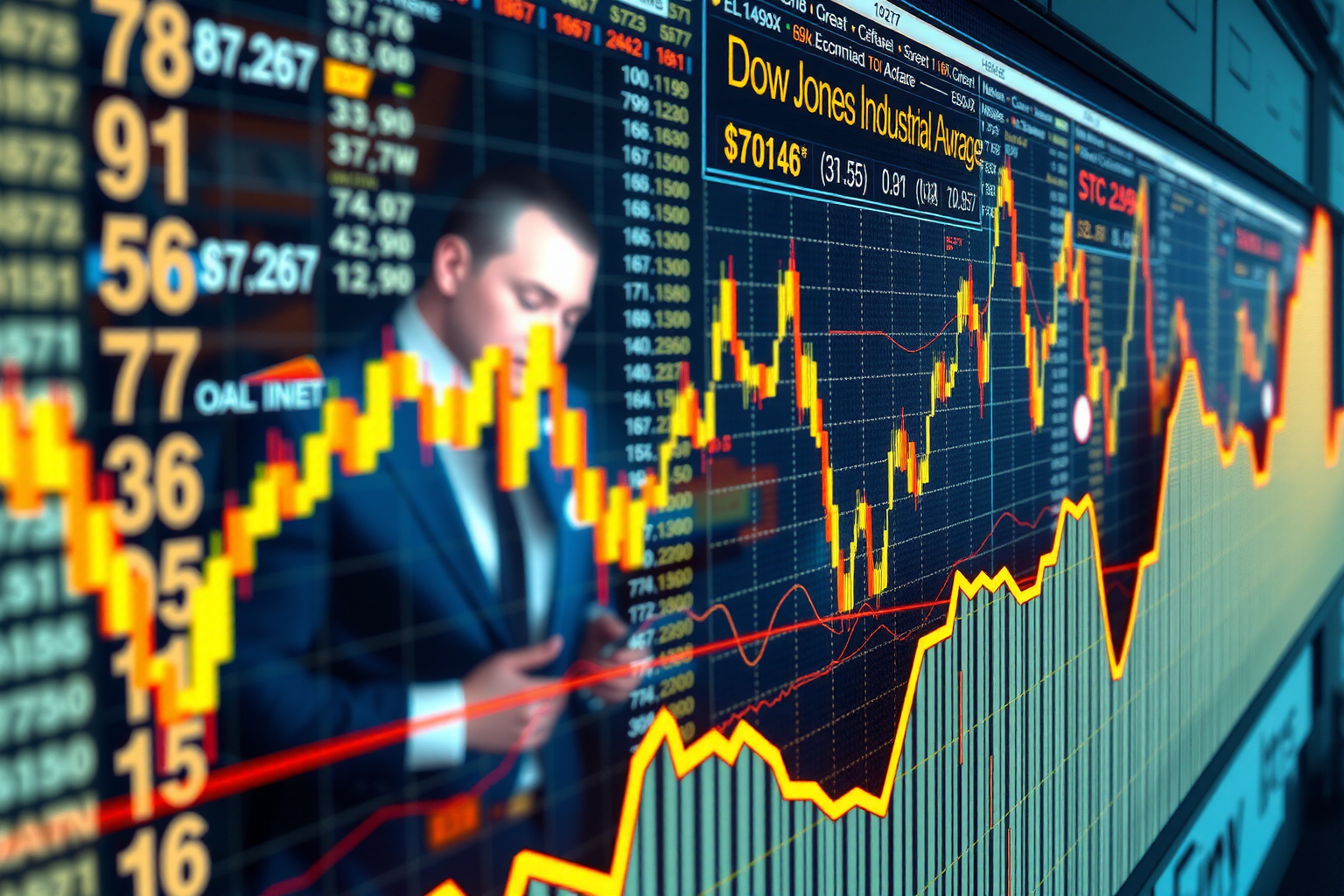
The Dow Jones Industrial Average, or DJIA, is one of the oldest and most well-known stock market indices in the United States. Established in 1896, the DJIA represents the performance of 30 prominent American companies, providing insights into the overall state of the U.S. stock market. It is a price-weighted index, with companies with higher stock prices having a greater impact on its movement. Despite some criticism, the DJIA remains a valuable tool for investors and analysts to track market trends and economic health. In this article, we will take a closer look at the history, composition, and significance of the DJIA.
Origins and Composition
It’s origins and composition, the Dow Jones Industrial Average (DJIA), a key indicator of stock market performance, traces its origins to the late 19th century. It was established by Charles Dow, a respected journalist and co-founder of the Wall Street Journal, as a means to track the performance of the industrial sector. Initially, the DJIA consisted of 12 companies, primarily representing the railroad industry. However, as the industrial landscape evolved, so did the index, leading to its current composition of 30 major companies across various sectors, such as technology, consumer goods, and financial services. This diverse range of incorporated businesses allows the DJIA to provide a comprehensive snapshot of the overall U.S. economy and its market trends.
Each of the companies included in the DJIA, often referred to as “the Dow,” is a significant player in its respective industry, and the collective performance of these companies is used to gauge the overall health of the stock market. The selection process for the DJIA is not arbitrary; it involves careful consideration and is overseen by the Averages Committee of S&P Dow Jones Indices, which is a joint venture between S&P Global, the CME Group, and News Corp. The committee aims to ensure that the index remains representative of the U.S. economy and the broader stock market, taking into account changing business dynamics and emerging industries.
Calculating the DJIA
The process of calculating the DJIA is distinct, with a methodology that sets it apart from other major stock market indices. Unlike the more commonly used market capitalization-weighted indices, the DJIA operates as a price-weighted index. This means that the companies in the index are weighted according to their stock price rather than their total market capitalization. As a result, the stock price of each component company directly influences the overall value of the DJIA, making it a unique and critical measurement tool in financial markets.
Everything you need to know about to maintain consistency and accuracy in its calculations, the DJIA employs a cornerstone known as the “Dow Divisor.” This divisor serves as a numerical constant that helps ensure the index’s stability and prevents abrupt changes in its value due to stock splits, special dividends, or other corporate actions. By integrating the Dow Divisor into its calculation, the DJIA can provide a reliable and comprehensive benchmark for measuring the performance of the 30 constituent companies and, consequently, the overall health of the U.S. stock market.
Price-Weighted Index Method
The DJIA’s classification as a price-weighted index has significant implications for its characteristics and historical performance. One of the primary distinctions is the skewing of influence, where companies with higher stock prices exert a more pronounced effect on the index’s movements. This price-weighted methodology can lead to scenarios where changes in the stock prices of companies with higher share values disproportionately affect the DJIA, potentially producing fluctuations that do not necessarily reflect the broader market’s pulse. As a result, the price-weighted approach remains a topic of ongoing discussion and analysis within the financial community.
Furthermore, being a price-weighted index means that even minor fluctuations in the stock prices of high-value companies can have a significant impact on the DJIA’s overall calculation. This characteristic differentiates the DJIA from market capitalization-weighted indices, which are less susceptible to abrupt and potentially misleading changes stemming from variations in the stock prices of individual companies within the index.
Changes to Components
The composition of the DJIA is not immutable; it undergoes periodic adjustments to ensure its continued relevance and accuracy in representing the U.S. economy and the stock market. These modifications to the index’s components reflect the dynamic nature of the business landscape and aim to address shifts in industry prominence and market dynamics. The inclusion of new companies and the removal of existing ones from the DJIA are strategic decisions made with a thorough assessment of the evolving economic environment and the performance benchmarks set by the index.
One significant example of this ongoing evolution occurred in November 2024, when Nvidia, a major player in the semiconductor industry, replaced Intel as one of the component companies in the DJIA. This shift underscored Nvidia’s rapid growth and its influential role in the technology sector, highlighting the DJIA’s proactive approach to remaining representative of the ever-changing dynamics in the U.S. economy. Such changes are instrumental in preserving the index’s status as a leading indicator of stock market performance and the economic landscape.
Notable Recent Additions
In recent years, the DJIA has witnessed notable additions that reflect the shifting dynamics and technological advancements shaping the U.S. economy. For instance, in February 2024, Amazon, a titan in the consumer retail sector, replaced Walgreens Boots Alliance in the index. This transition marked a significant acknowledgment of Amazon’s expanding influence and its pivotal role in reshaping the retail landscape, indicating the DJIA’s responsiveness to transformative industry trends. The inclusion of such influential and market-shaping companies further underscores the DJIA’s stature as an authoritative benchmark for the U.S. stock market.
Likewise, Nvidia’s replacement of Intel in the DJIA in November 2024 represented a noteworthy development, signifying the ascent of up-and-coming technology companies and their growing prominence in the stock market. These changes to the index’s composition demonstrate its adaptive nature and the ongoing efforts to ensure its continued effectiveness in capturing the pulse of the U.S. economy and the evolving business environment. Such strategic modifications play a critical role in maintaining the DJIA’s relevance and reliability as a key barometer for stock market performance.
The Criticism
While the DJIA holds a revered position as a stalwart indicator of the U.S. stock market, it has not been immune to criticism regarding its inherent characteristics and limitations. One of the primary points of contention revolves around its classification as a price-weighted index, which can inadvertently lead to an overemphasis on the performance of higher-priced stocks while diminishing the impact of companies with lower stock prices. This disproportionate influence has raised concerns about the index’s ability to accurately reflect the overall market’s dynamics and the performance of a comprehensive range of constituent companies.
Moreover, the relatively limited number of companies—30 in total—constituting the DJIA has sparked debates about its capacity to comprehensively represent the U.S. stock market as a whole. Critics argue that the index’s narrow focus may potentially overlook key industries and market segments, leading to a less holistic portrayal of the broader market’s performance. These critiques have prompted ongoing discussions about the suitability of the DJIA’s structure and its capacity to serve as a reliable and encompassing gauge of the U.S. stock market’s health and trends.
The Other Major Indices
In addition to the DJIA, the S&P 500 and the Nasdaq Composite are integral players in the landscape of major stock market indices, each possessing distinct characteristics and methodologies that distinguish them from one another. The S&P 500, comprising 500 large-cap U.S. companies, employs a market capitalization-weighted approach, allowing it to encompass a diverse array of industries and sectors, making it a comprehensive indicator of the U.S. stock market’s performance.
On the other hand, the Nasdaq Composite is renowned for its heavy weighting in technology and growth-oriented companies, rendering it a critical benchmark for the technology sector’s performance and innovation. Unlike the DJIA’s price-weighted methodology, the Nasdaq Composite operates as a market capitalization-weighted index, aligning its performance more closely with the overall market capitalization of the companies it comprises. This divergence in index composition and weighting methodologies provides investors with a diverse set of tools and benchmarks to assess and analyze the U.S. stock market’s dynamics and individual sectoral performances.
DJIA as an Economic Barometer
Despite its criticisms and limitations, the DJIA continues to hold a pivotal position as an economic barometer and a key point of reference for gauging the health of the U.S. stock market and the overall economy. Its historical significance, coupled with its stature as one of the most closely monitored stock indices, solidifies its status as an invaluable tool for investors, analysts, and economists alike. Whether tracking its movements on a daily basis or utilizing its historical data for long-term economic analysis, the DJIA remains an indispensable lens through which to view the evolving landscape of the U.S. economy and its market dynamics.
Furthermore, the DJIA’s composition of 30 leading companies from diverse industries further enhances its capacity to offer insightful perspectives on the U.S. economy. Spanning sectors such as technology, finance, healthcare, and consumer goods, the index serves as a microcosm of the American business landscape, reflecting the performance and trends of key industry players. As such, it continues to play a pivotal role in shaping investment decisions, guiding economic forecasts, and providing a comprehensive window into the ever-changing dynamics of the U.S. stock market and the economy at large.
In summary, the Dow Jones Industrial Average’s rich history, distinct calculation method, recent additions, and position within the broader landscape of major stock market indices collectively underline its enduring significance as a paramount barometer of the U.S. economy and the stock market’s performance. While it has faced criticism and undergone notable changes, its stature and relevance persist, solidifying its indispensable role in the realm of financial markets and economic analysis.
Key Takeaways
The Dow Jones Industrial Average (DJIA) stands as a pivotal barometer for the U.S. stock market and the overall economy, offering insights into the performance of 30 influential companies. Its distinct price-weighted index method and historical significance further underscore its enduring importance, while recent additions to its components reflect its adaptability and relevance in capturing the dynamic landscape of the U.S. economy. Despite facing criticism for its methodology and composition, the DJIA remains an invaluable tool for investors, analysts, and economists, providing a comprehensive lens through which to assess market trends and economic health. Its capacity to influence investment decisions, guide economic forecasts, and offer a multifaceted perspective on the U.S. stock market solidifies its position as a key barometer within the realm of financial markets and economic analysis.
The DJIA’s evolution, including notable recent additions and its responsive approach to industry changes, exemplifies its continuous adaptation to remain a reliable and authoritative measure of the U.S. stock market’s performance. Whether considering the historical impact of its components or its ongoing relevance in shaping market dynamics, the DJIA’s enduring significance offers a compelling narrative of its indispensable role in the ever-changing landscape of the U.S. economy and the stock market at large.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Dow Jones Industrial Average, or DJIA, is an iconic and historic stock market index that tracks the performance of 30 leading American companies. While it has faced criticism for its price-weighted methodology and its limited representation of the market, it remains a valuable tool for investors and analysts to monitor economic trends and the state of the U.S. economy. With recent changes in its components, the DJIA continues to evolve and adapt to reflect the current economic landscape.